|
Calcium
Waves |
|
The following
movies show intercellular Ca2+ waves as they propagate through
networks of astrocytes and Müller cells at the vitreal surface of
the rat retina. Glial cells were labeled with a Ca2+
indicator dye (Fluo-4 AM or Calcium Green-1 AM) and were imaged with a
video-rate confocal microscope. Waves were initiated with a mechanical
stimulus, a 10 msec, 15 to 25 mm pulse.
Download
QuickTime
Player if you don't have it already installed. |
|
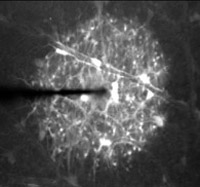
Low magnification view of Ca2+
wave propagation. Stimulation of an astrocyte soma initiates a Ca2+
wave which propagates outwards symmetrically from the point of stimulation.
The wave propagates through both astrocytes (large polymorphic cells) and
Müller cell endfeet (smaller, round profiles). The video is shown
at 0.75 times normal speed. Width of image, 335 mm.
(QuickTime clip, 2.3 MB.) |
|
|
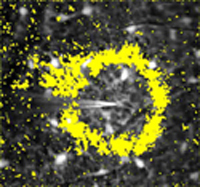
Propagation of the leading edge
of a Ca2+ wave. A fluorescence image of dye-labeled astrocytes
and Müller cells is shown in black and white. The superimposed yellow
regions mark the leading edge of the Ca2+ wave (where change
in fluorescence between successive images exceeded a threshold value). Video
shown at normal speed. Width of image, 240 mm.
From Newman
and Zahs, Science, 275:844-847, 1997. (QuickTime clip, 649 KB.) |
|
|
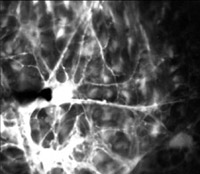
High magnification
view of Ca2+ wave propagation. Stimulation of an astrocyte
soma initiates a Ca2+ wave which begins in the stimulated soma
and propagates smoothly through the processes of the astrocyte and into
adjacent astrocytes. After a delay of ~1 sec, the wave also propagates
into neighboring Müller cell endfeet (dimmer round profiles). Video
shown at 0.75 times normal speed. Width of image, 150 mm.
From Newman,
J Neurosci. 21:2215-23,
2001. (QuickTime clip, 2.5 MB.) |
|
|
|
|
|